Bayesian Supervised Learning with Heteroskedasticity in StochTree
Source:vignettes/Heteroskedasticity.Rmd
Heteroskedasticity.RmdThis vignette demonstrates how to use the bart()
function for Bayesian supervised learning (Chipman, George, and McCulloch (2010)) and
causal inference (Hahn, Murray, and Carvalho
(2020)), with an additional “variance forest,” for modeling
conditional variance (see Murray (2021)).
To begin, we load the stochtree package.
Section 1: Supervised Learning
Demo 1: Variance-Only Simulation (simple DGP)
Simulation
Here, we generate data with a constant (zero) mean and a relatively simple covariate-modified variance function.
# Generate the data
n <- 500
p_x <- 10
X <- matrix(runif(n*p_x), ncol = p_x)
f_XW <- 0
s_XW <- (
((0 <= X[,1]) & (0.25 > X[,1])) * (0.5) +
((0.25 <= X[,1]) & (0.5 > X[,1])) * (1) +
((0.5 <= X[,1]) & (0.75 > X[,1])) * (2) +
((0.75 <= X[,1]) & (1 > X[,1])) * (3)
)
y <- f_XW + rnorm(n, 0, 1)*s_XW
# Split data into test and train sets
test_set_pct <- 0.2
n_test <- round(test_set_pct*n)
n_train <- n - n_test
test_inds <- sort(sample(1:n, n_test, replace = FALSE))
train_inds <- (1:n)[!((1:n) %in% test_inds)]
X_test <- as.data.frame(X[test_inds,])
X_train <- as.data.frame(X[train_inds,])
y_test <- y[test_inds]
y_train <- y[train_inds]
f_x_test <- f_XW[test_inds]
f_x_train <- f_XW[train_inds]
s_x_test <- s_XW[test_inds]
s_x_train <- s_XW[train_inds]Sampling and Analysis
Warmstart
We first sample the
ensemble using “warm-start” initialization (He
and Hahn (2023)). This is the default in
stochtree.
num_gfr <- 10
num_burnin <- 0
num_mcmc <- 100
num_trees <- 20
a_0 <- 1.5
num_samples <- num_gfr + num_burnin + num_mcmc
general_params <- list(sample_sigma2_global = F)
mean_forest_params <- list(sample_sigma2_leaf = F, num_trees = 0)
variance_forest_params <- list(num_trees = num_trees)
bart_model_warmstart <- stochtree::bart(
X_train = X_train, y_train = y_train, X_test = X_test,
num_gfr = num_gfr, num_burnin = num_burnin, num_mcmc = num_mcmc,
general_params = general_params, mean_forest_params = mean_forest_params,
variance_forest_params = variance_forest_params
)Inspect the MCMC samples
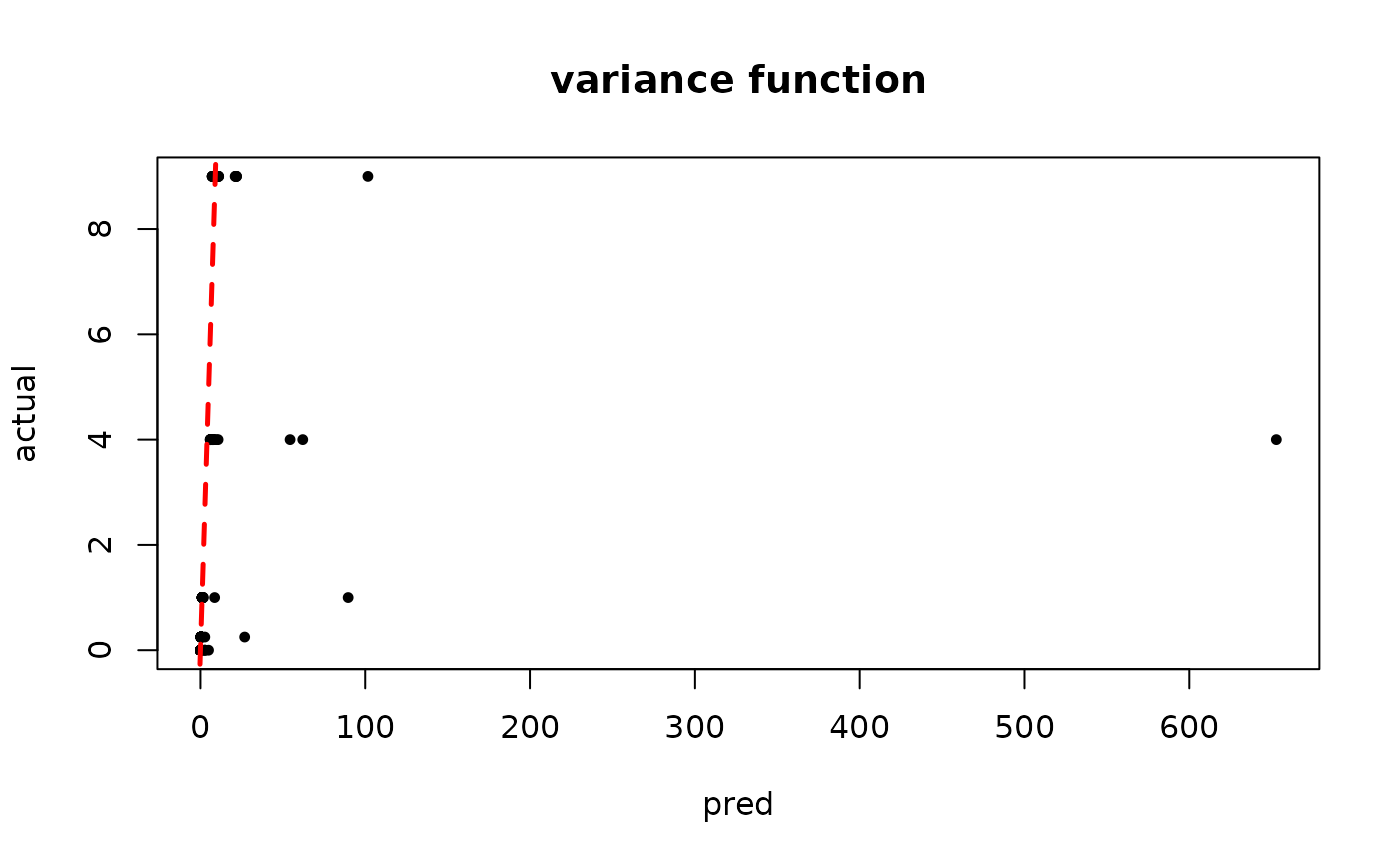
plot(rowMeans(bart_model_warmstart$sigma2_x_hat_test), s_x_test^2,
pch=16, cex=0.75, xlab = "pred", ylab = "actual", main = "variance function")
abline(0,1,col="red",lty=2,lwd=2.5)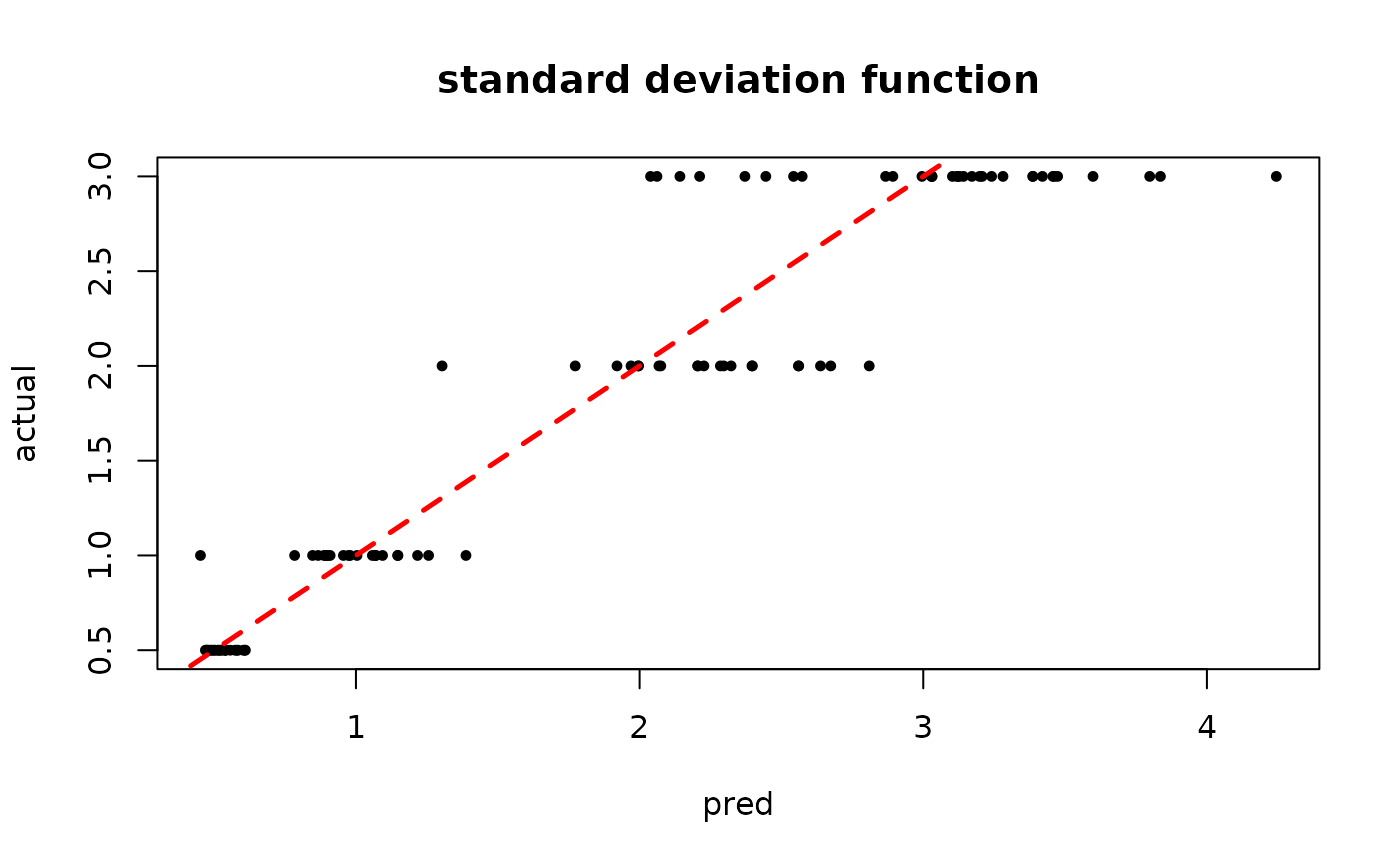
MCMC
We now sample the ensemble using MCMC with root initialization (as in Chipman, George, and McCulloch (2010)).
num_gfr <- 0
num_burnin <- 1000
num_mcmc <- 100
num_samples <- num_gfr + num_burnin + num_mcmc
general_params <- list(sample_sigma2_global = F)
mean_forest_params <- list(sample_sigma2_leaf = F, num_trees = 0)
variance_forest_params <- list(num_trees = num_trees)
bart_model_mcmc <- stochtree::bart(
X_train = X_train, y_train = y_train, X_test = X_test,
num_gfr = num_gfr, num_burnin = num_burnin, num_mcmc = num_mcmc,
general_params = general_params, mean_forest_params = mean_forest_params,
variance_forest_params = variance_forest_params
)Inspect the MCMC samples
plot(rowMeans(bart_model_mcmc$sigma2_x_hat_test), s_x_test^2,
pch=16, cex=0.75, xlab = "pred", ylab = "actual", main = "variance function")
abline(0,1,col="red",lty=2,lwd=2.5)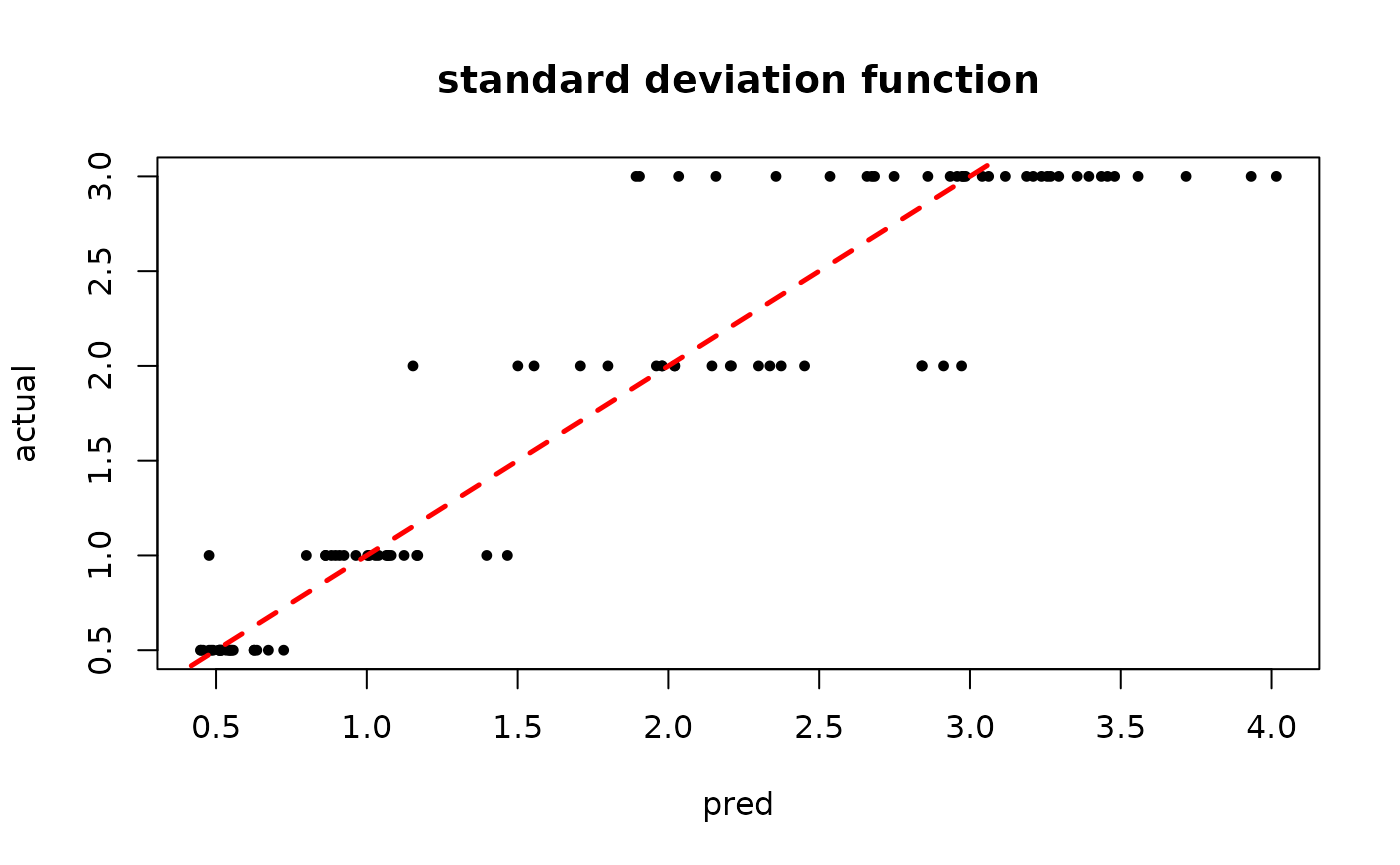
Demo 2: Variance-Only Simulation (complex DGP)
Simulation
Here, we generate data with a constant (zero) mean and a more complex covariate-modified variance function.
# Generate the data
n <- 500
p_x <- 10
X <- matrix(runif(n*p_x), ncol = p_x)
f_XW <- 0
s_XW <- (
((0 <= X[,1]) & (0.25 > X[,1])) * (0.5*X[,3]) +
((0.25 <= X[,1]) & (0.5 > X[,1])) * (1*X[,3]) +
((0.5 <= X[,1]) & (0.75 > X[,1])) * (2*X[,3]) +
((0.75 <= X[,1]) & (1 > X[,1])) * (3*X[,3])
)
y <- f_XW + rnorm(n, 0, 1)*s_XW
# Split data into test and train sets
test_set_pct <- 0.2
n_test <- round(test_set_pct*n)
n_train <- n - n_test
test_inds <- sort(sample(1:n, n_test, replace = FALSE))
train_inds <- (1:n)[!((1:n) %in% test_inds)]
X_test <- as.data.frame(X[test_inds,])
X_train <- as.data.frame(X[train_inds,])
y_test <- y[test_inds]
y_train <- y[train_inds]
f_x_test <- f_XW[test_inds]
f_x_train <- f_XW[train_inds]
s_x_test <- s_XW[test_inds]
s_x_train <- s_XW[train_inds]Sampling and Analysis
Warmstart
We first sample the
ensemble using “warm-start” initialization (He
and Hahn (2023)). This is the default in
stochtree.
num_trees <- 20
num_gfr <- 10
num_burnin <- 0
num_mcmc <- 100
num_samples <- num_gfr + num_burnin + num_mcmc
general_params <- list(sample_sigma2_global = F)
mean_forest_params <- list(sample_sigma2_leaf = F, num_trees = 0,
alpha = 0.95, beta = 2, min_samples_leaf = 5)
variance_forest_params <- list(num_trees = num_trees, alpha = 0.95,
beta = 1.25, min_samples_leaf = 1)
bart_model_warmstart <- stochtree::bart(
X_train = X_train, y_train = y_train, X_test = X_test,
num_gfr = num_gfr, num_burnin = num_burnin, num_mcmc = num_mcmc,
general_params = general_params, mean_forest_params = mean_forest_params,
variance_forest_params = variance_forest_params
)Inspect the MCMC samples
plot(rowMeans(bart_model_warmstart$sigma2_x_hat_test), s_x_test^2,
pch=16, cex=0.75, xlab = "pred", ylab = "actual", main = "variance function")
abline(0,1,col="red",lty=2,lwd=2.5)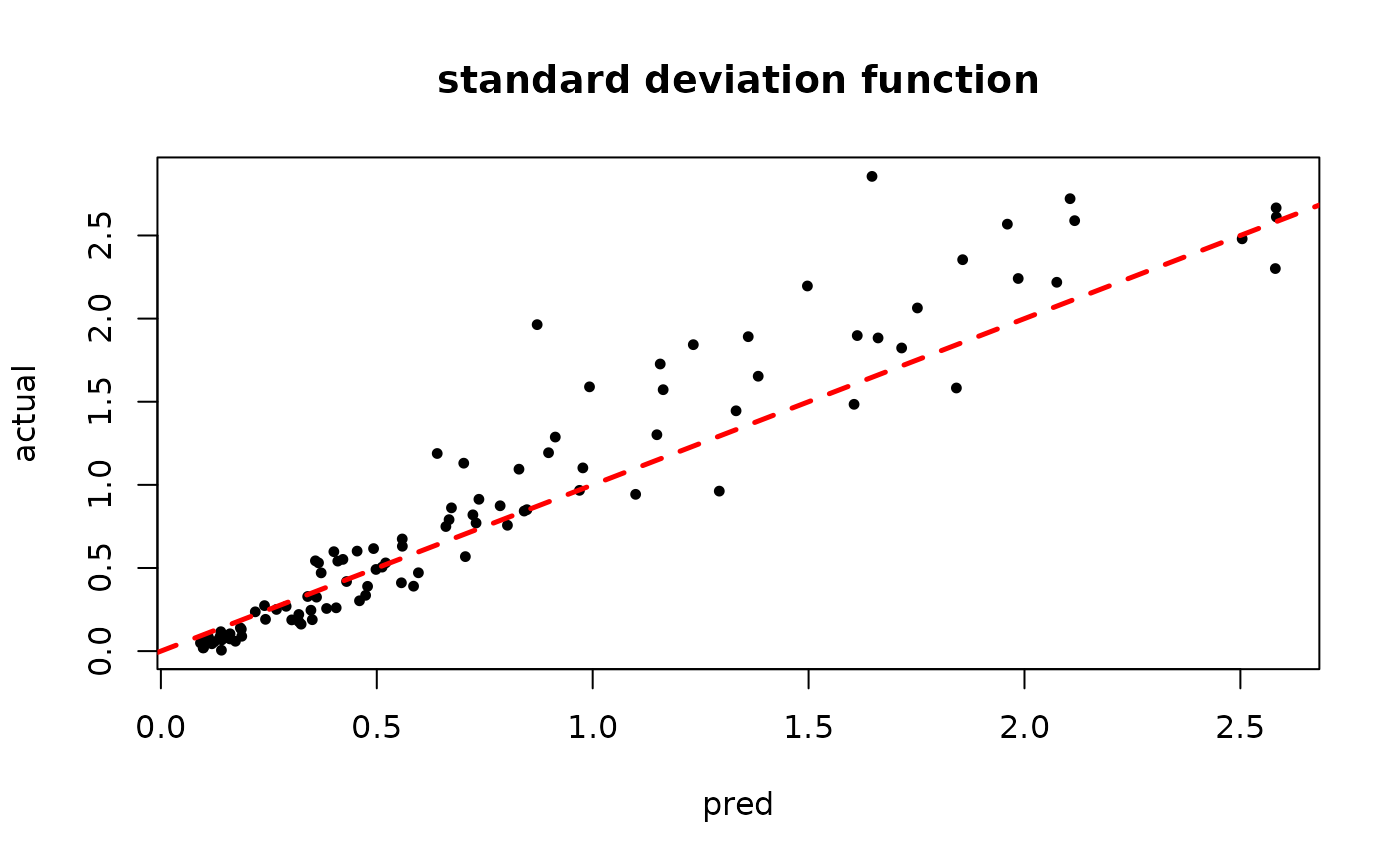
MCMC
We now sample the ensemble using MCMC with root initialization (as in Chipman, George, and McCulloch (2010)).
num_gfr <- 0
num_burnin <- 1000
num_mcmc <- 100
num_samples <- num_gfr + num_burnin + num_mcmc
general_params <- list(sample_sigma2_global = F)
mean_forest_params <- list(sample_sigma2_leaf = F, num_trees = 0,
alpha = 0.95, beta = 2, min_samples_leaf = 5)
variance_forest_params <- list(num_trees = num_trees, alpha = 0.95,
beta = 1.25, min_samples_leaf = 1)
bart_model_mcmc <- stochtree::bart(
X_train = X_train, y_train = y_train, X_test = X_test,
num_gfr = num_gfr, num_burnin = num_burnin, num_mcmc = num_mcmc,
general_params = general_params, mean_forest_params = mean_forest_params,
variance_forest_params = variance_forest_params
)Inspect the MCMC samples
plot(rowMeans(bart_model_mcmc$sigma2_x_hat_test), s_x_test^2,
pch=16, cex=0.75, xlab = "pred", ylab = "actual", main = "variance function")
abline(0,1,col="red",lty=2,lwd=2.5)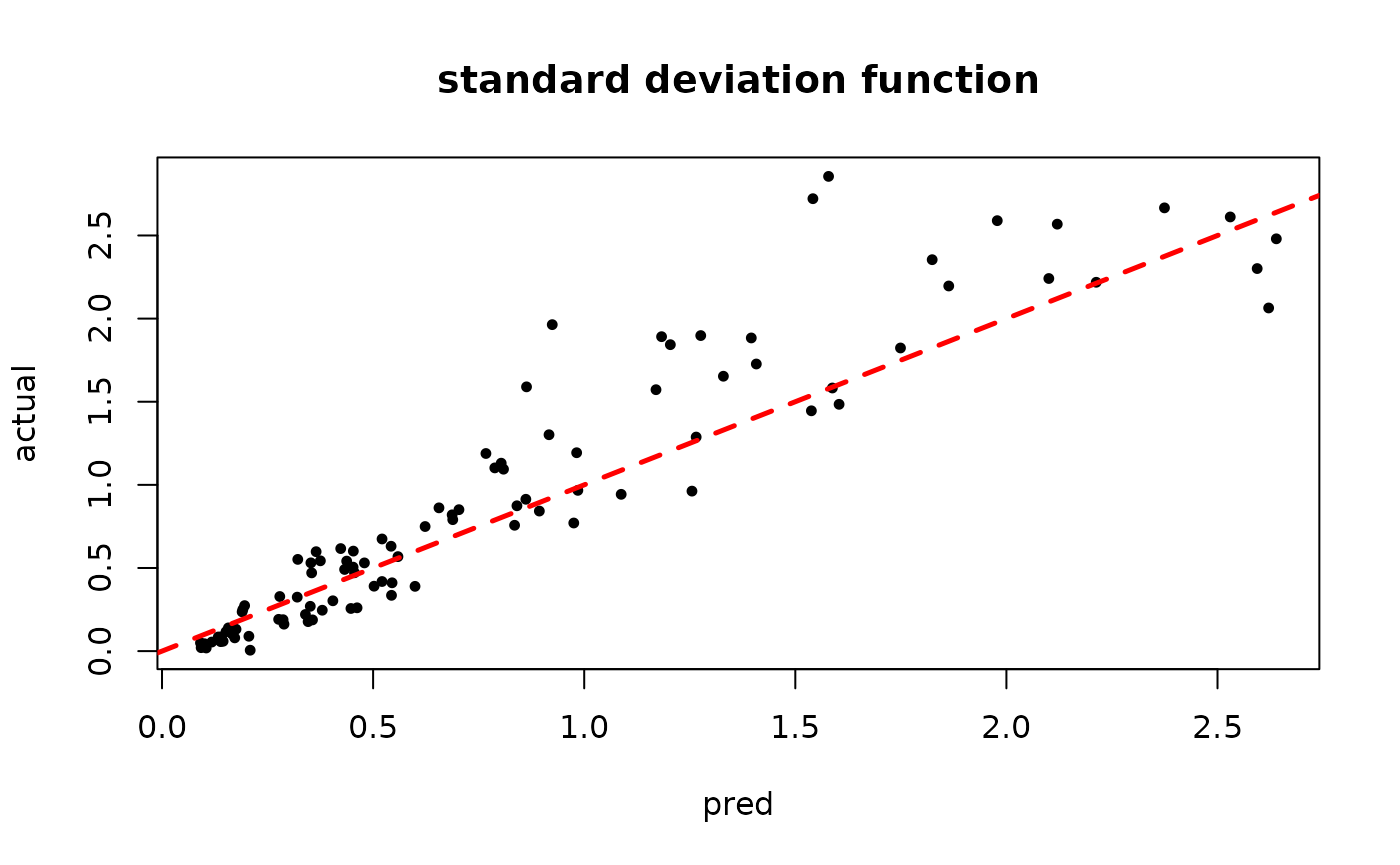
Demo 3: Mean and Variance Simulation (simple DGP)
Simulation
Here, we generate data with (relatively simple) covariate-modified mean and variance functions.
# Generate the data
n <- 500
p_x <- 10
X <- matrix(runif(n*p_x), ncol = p_x)
f_XW <- (
((0 <= X[,2]) & (0.25 > X[,2])) * (-6) +
((0.25 <= X[,2]) & (0.5 > X[,2])) * (-2) +
((0.5 <= X[,2]) & (0.75 > X[,2])) * (2) +
((0.75 <= X[,2]) & (1 > X[,2])) * (6)
)
s_XW <- (
((0 <= X[,1]) & (0.25 > X[,1])) * (0.5) +
((0.25 <= X[,1]) & (0.5 > X[,1])) * (1) +
((0.5 <= X[,1]) & (0.75 > X[,1])) * (2) +
((0.75 <= X[,1]) & (1 > X[,1])) * (3)
)
y <- f_XW + rnorm(n, 0, 1)*s_XW
# Split data into test and train sets
test_set_pct <- 0.2
n_test <- round(test_set_pct*n)
n_train <- n - n_test
test_inds <- sort(sample(1:n, n_test, replace = FALSE))
train_inds <- (1:n)[!((1:n) %in% test_inds)]
X_test <- as.data.frame(X[test_inds,])
X_train <- as.data.frame(X[train_inds,])
y_test <- y[test_inds]
y_train <- y[train_inds]
f_x_test <- f_XW[test_inds]
f_x_train <- f_XW[train_inds]
s_x_test <- s_XW[test_inds]
s_x_train <- s_XW[train_inds]Sampling and Analysis
Warmstart
We first sample the
ensemble using “warm-start” initialization (He
and Hahn (2023)). This is the default in
stochtree.
num_gfr <- 10
num_burnin <- 0
num_mcmc <- 100
num_samples <- num_gfr + num_burnin + num_mcmc
general_params <- list(sample_sigma2_global = F)
mean_forest_params <- list(sample_sigma2_leaf = F, num_trees = 50,
alpha = 0.95, beta = 2, min_samples_leaf = 5)
variance_forest_params <- list(num_trees = 50, alpha = 0.95,
beta = 1.25, min_samples_leaf = 5)
bart_model_warmstart <- stochtree::bart(
X_train = X_train, y_train = y_train, X_test = X_test,
num_gfr = num_gfr, num_burnin = num_burnin, num_mcmc = num_mcmc,
general_params = general_params, mean_forest_params = mean_forest_params,
variance_forest_params = variance_forest_params
)Inspect the MCMC samples
plot(rowMeans(bart_model_warmstart$y_hat_test), y_test,
pch=16, cex=0.75, xlab = "pred", ylab = "actual", main = "mean function")
abline(0,1,col="red",lty=2,lwd=2.5)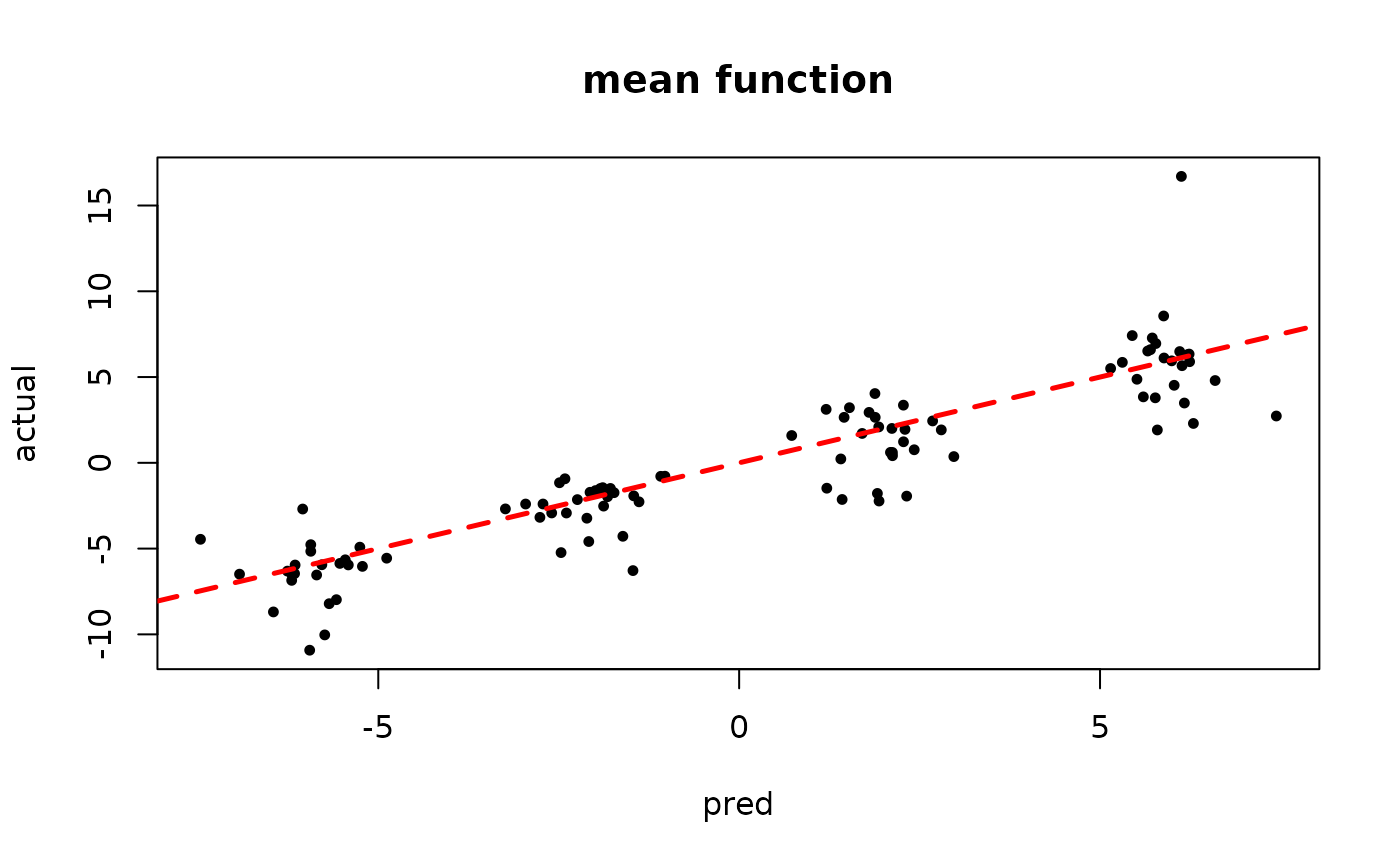
plot(rowMeans(bart_model_warmstart$sigma2_x_hat_test), s_x_test^2,
pch=16, cex=0.75, xlab = "pred", ylab = "actual", main = "variance function")
abline(0,1,col="red",lty=2,lwd=2.5)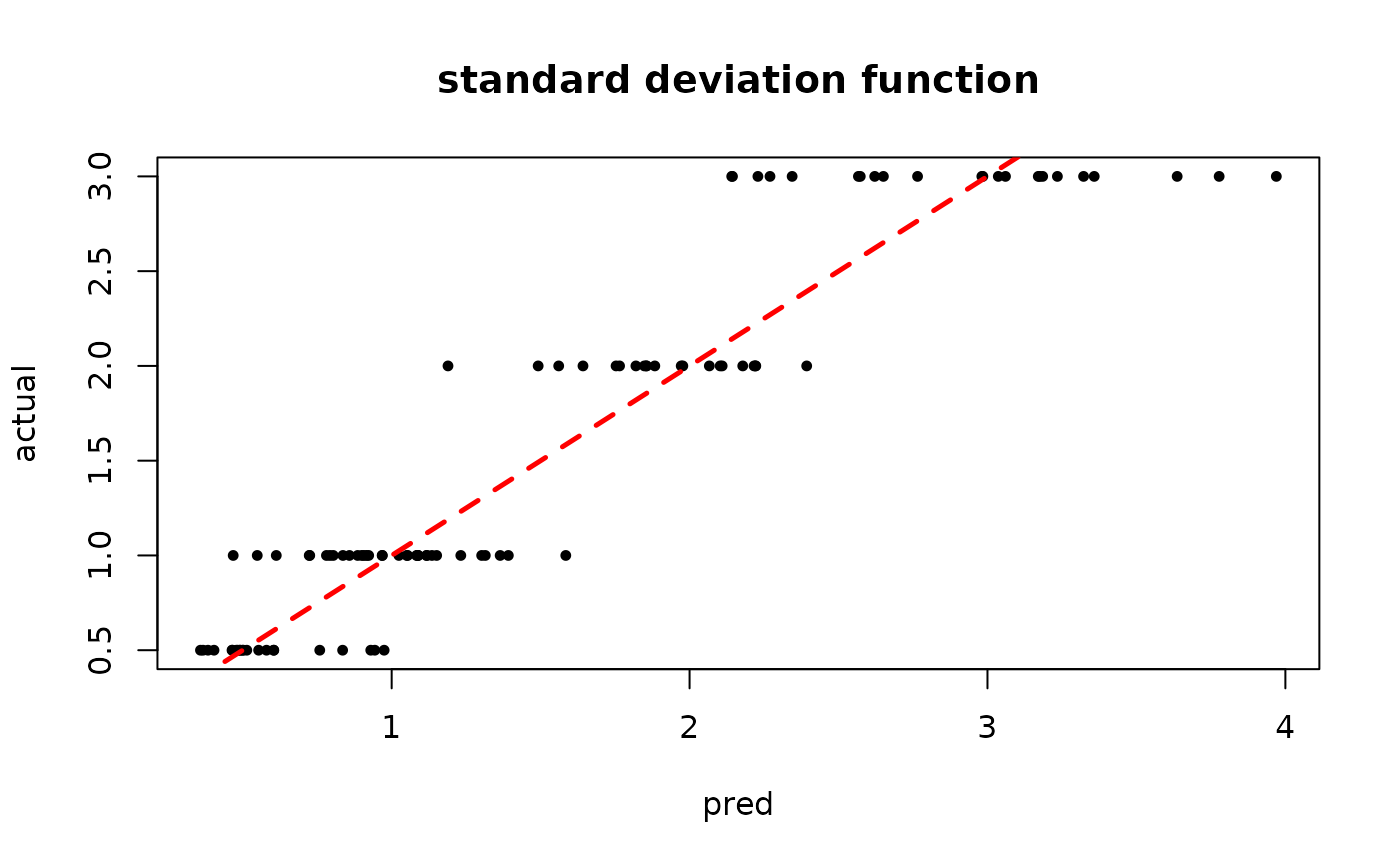
MCMC
We now sample the ensemble using MCMC with root initialization (as in Chipman, George, and McCulloch (2010)).
num_gfr <- 0
num_burnin <- 1000
num_mcmc <- 100
num_samples <- num_gfr + num_burnin + num_mcmc
general_params <- list(sample_sigma2_global = F)
mean_forest_params <- list(sample_sigma2_leaf = F, num_trees = 50,
alpha = 0.95, beta = 2, min_samples_leaf = 5)
variance_forest_params <- list(num_trees = 50, alpha = 0.95,
beta = 1.25, min_samples_leaf = 5)
bart_model_mcmc <- stochtree::bart(
X_train = X_train, y_train = y_train, X_test = X_test,
num_gfr = num_gfr, num_burnin = num_burnin, num_mcmc = num_mcmc,
general_params = general_params, mean_forest_params = mean_forest_params,
variance_forest_params = variance_forest_params
)Inspect the MCMC samples
plot(rowMeans(bart_model_mcmc$y_hat_test), y_test,
pch=16, cex=0.75, xlab = "pred", ylab = "actual", main = "mean function")
abline(0,1,col="red",lty=2,lwd=2.5)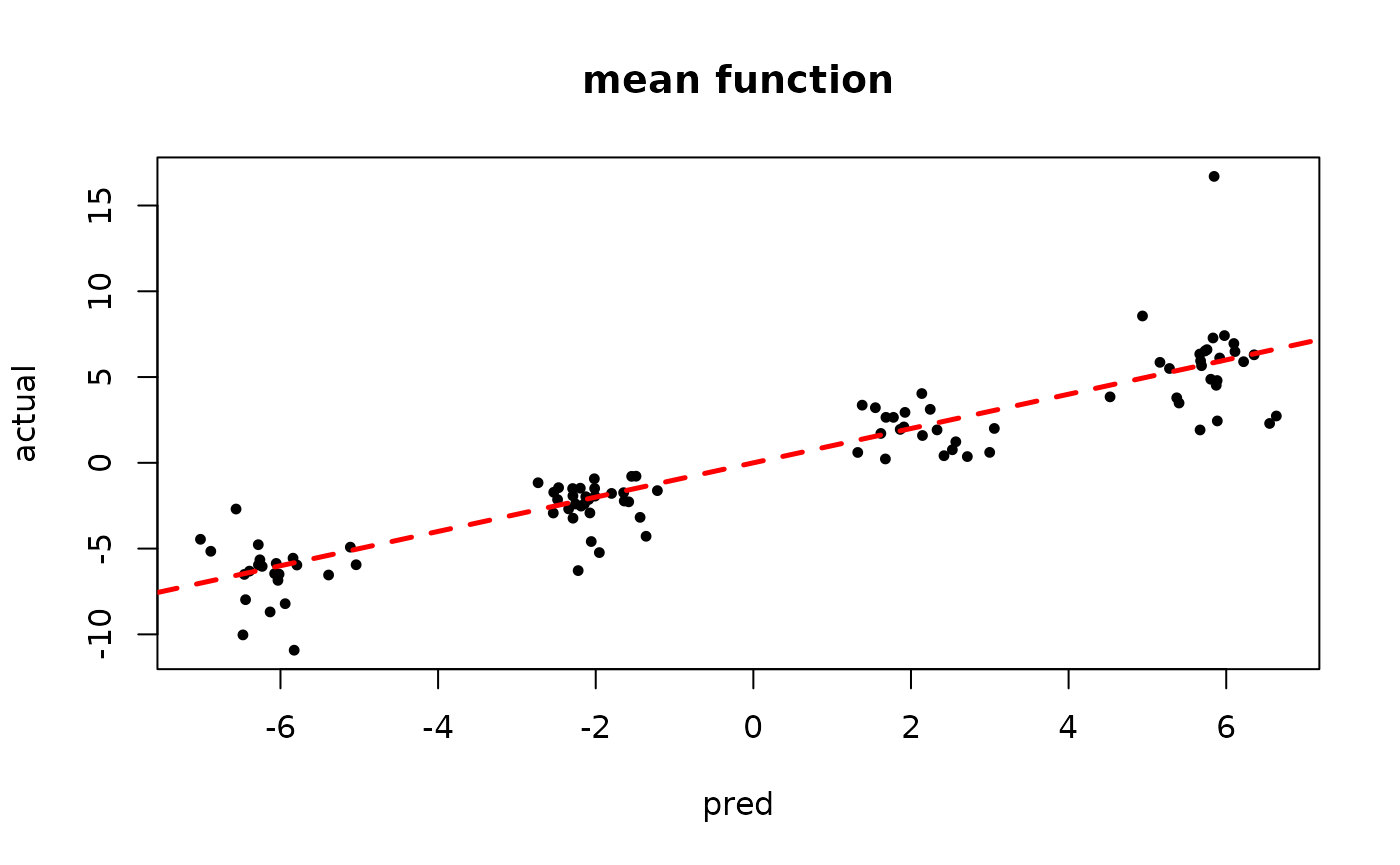
plot(rowMeans(bart_model_mcmc$sigma2_x_hat_test), s_x_test^2,
pch=16, cex=0.75, xlab = "pred", ylab = "actual", main = "variance function")
abline(0,1,col="red",lty=2,lwd=2.5)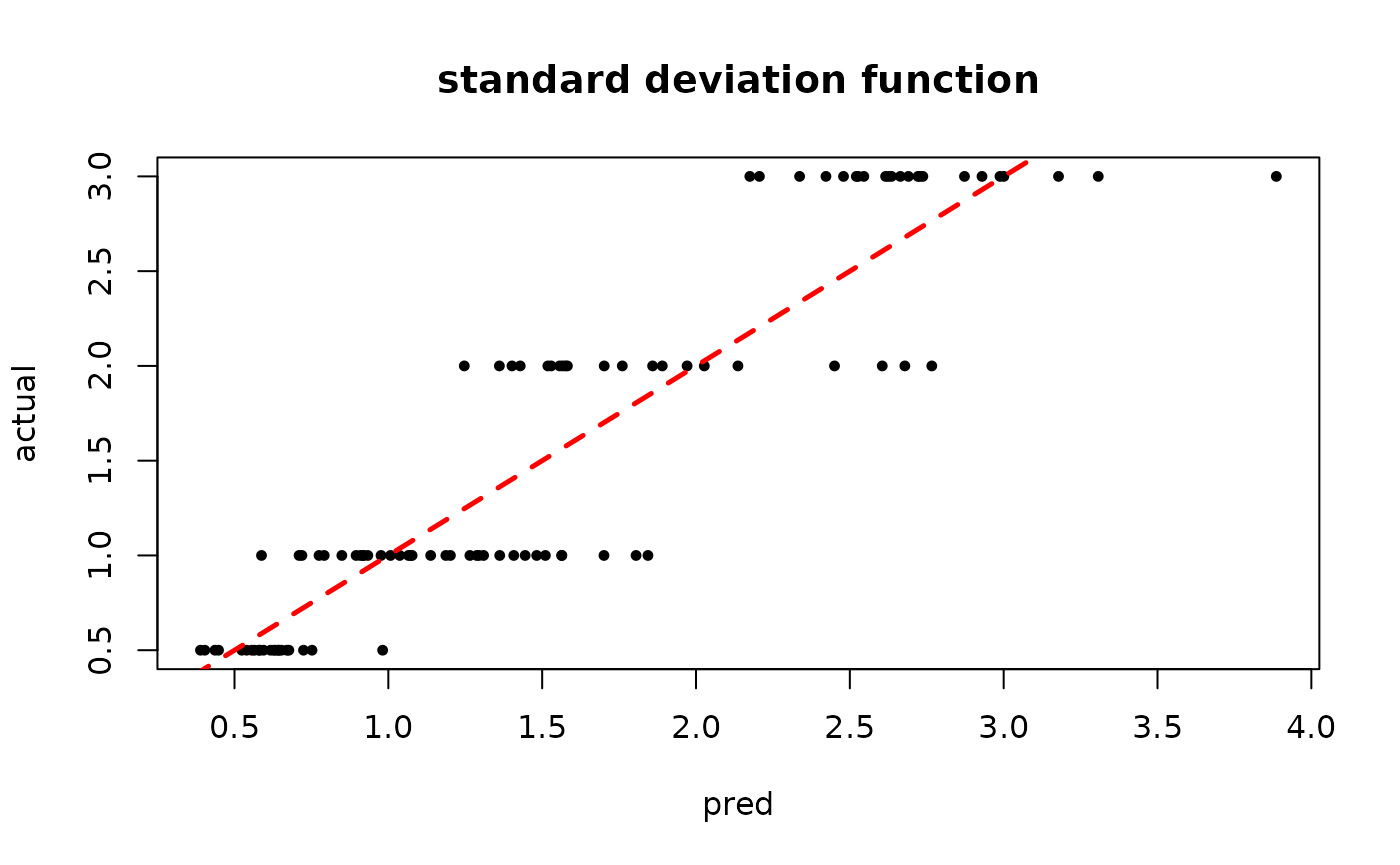
Demo 4: Mean and Variance Simulation (complex DGP)
Simulation
Here, we generate data with more complex covariate-modified mean and variance functions.
# Generate the data
n <- 500
p_x <- 10
X <- matrix(runif(n*p_x), ncol = p_x)
f_XW <- (
((0 <= X[,2]) & (0.25 > X[,2])) * (-6*X[,4]) +
((0.25 <= X[,2]) & (0.5 > X[,2])) * (-2*X[,4]) +
((0.5 <= X[,2]) & (0.75 > X[,2])) * (2*X[,4]) +
((0.75 <= X[,2]) & (1 > X[,2])) * (6*X[,4])
)
s_XW <- (
((0 <= X[,1]) & (0.25 > X[,1])) * (0.5*X[,3]) +
((0.25 <= X[,1]) & (0.5 > X[,1])) * (1*X[,3]) +
((0.5 <= X[,1]) & (0.75 > X[,1])) * (2*X[,3]) +
((0.75 <= X[,1]) & (1 > X[,1])) * (3*X[,3])
)
y <- f_XW + rnorm(n, 0, 1)*s_XW
# Split data into test and train sets
test_set_pct <- 0.2
n_test <- round(test_set_pct*n)
n_train <- n - n_test
test_inds <- sort(sample(1:n, n_test, replace = FALSE))
train_inds <- (1:n)[!((1:n) %in% test_inds)]
X_test <- as.data.frame(X[test_inds,])
X_train <- as.data.frame(X[train_inds,])
y_test <- y[test_inds]
y_train <- y[train_inds]
f_x_test <- f_XW[test_inds]
f_x_train <- f_XW[train_inds]
s_x_test <- s_XW[test_inds]
s_x_train <- s_XW[train_inds]Sampling and Analysis
Warmstart
We first sample the
ensemble using “warm-start” initialization (He
and Hahn (2023)). This is the default in
stochtree.
num_gfr <- 10
num_burnin <- 0
num_mcmc <- 100
num_samples <- num_gfr + num_burnin + num_mcmc
general_params <- list(sample_sigma2_global = F)
mean_forest_params <- list(sample_sigma2_leaf = F, num_trees = 50,
alpha = 0.95, beta = 2, min_samples_leaf = 5)
variance_forest_params <- list(num_trees = 50, alpha = 0.95,
beta = 1.25, min_samples_leaf = 5)
bart_model_warmstart <- stochtree::bart(
X_train = X_train, y_train = y_train, X_test = X_test,
num_gfr = num_gfr, num_burnin = num_burnin, num_mcmc = num_mcmc,
general_params = general_params, mean_forest_params = mean_forest_params,
variance_forest_params = variance_forest_params
)Inspect the MCMC samples
plot(rowMeans(bart_model_warmstart$y_hat_test), y_test,
pch=16, cex=0.75, xlab = "pred", ylab = "actual", main = "mean function")
abline(0,1,col="red",lty=2,lwd=2.5)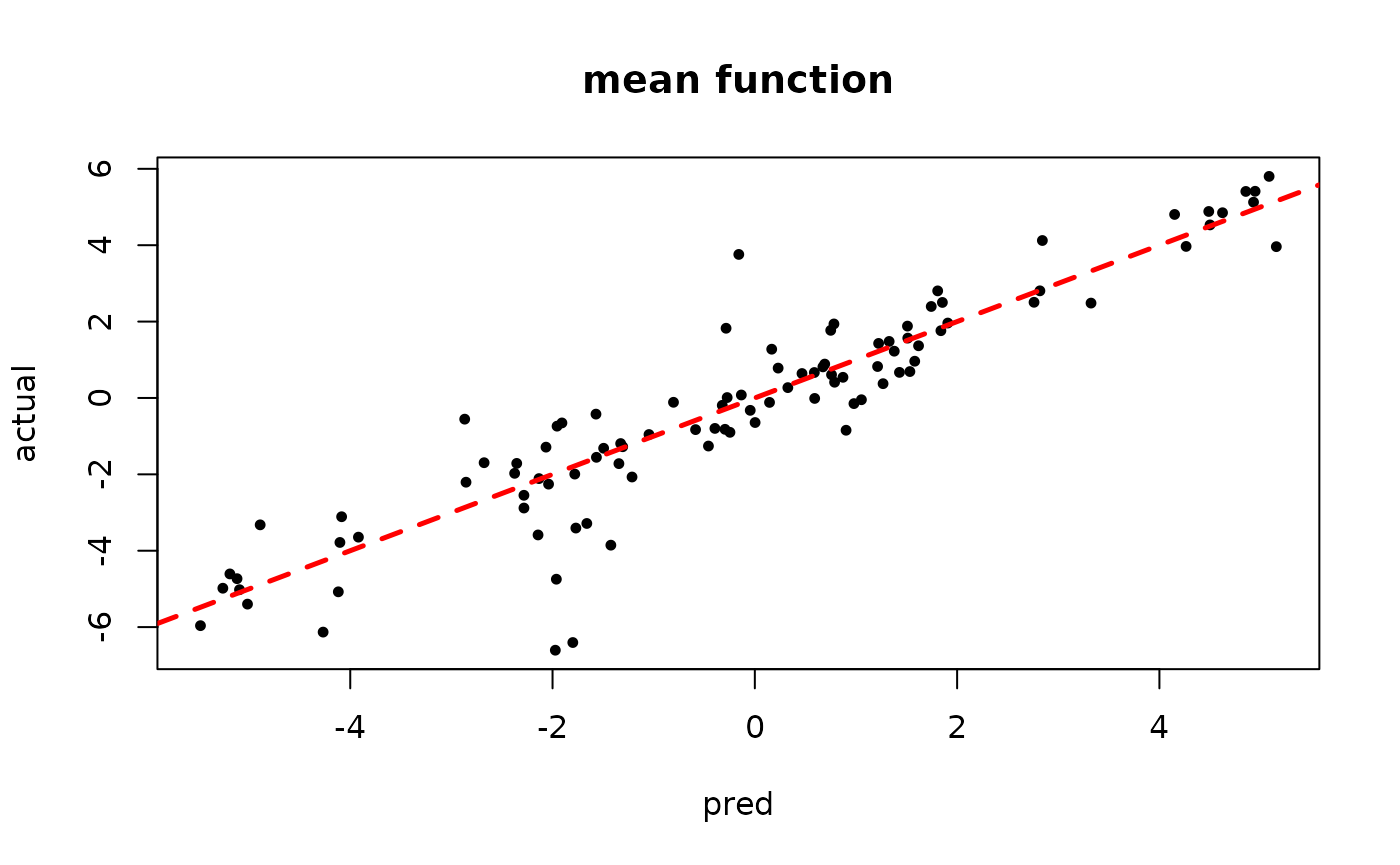
plot(rowMeans(bart_model_warmstart$sigma2_x_hat_test), s_x_test^2,
pch=16, cex=0.75, xlab = "pred", ylab = "actual", main = "variance function")
abline(0,1,col="red",lty=2,lwd=2.5)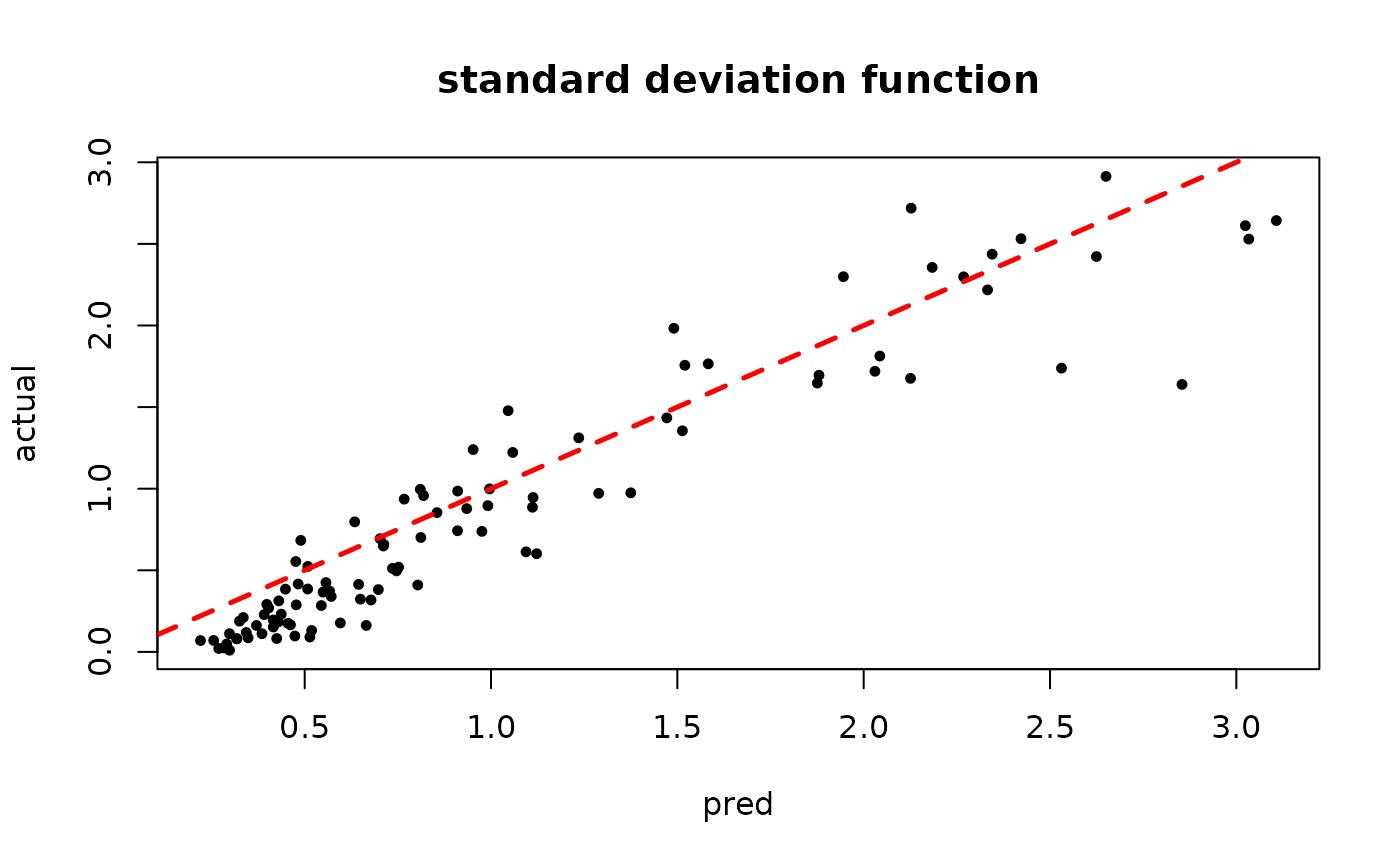
MCMC
We now sample the ensemble using MCMC with root initialization (as in Chipman, George, and McCulloch (2010)).
num_gfr <- 0
num_burnin <- 1000
num_mcmc <- 100
num_samples <- num_gfr + num_burnin + num_mcmc
general_params <- list(sample_sigma2_global = F)
mean_forest_params <- list(sample_sigma2_leaf = F, num_trees = 50,
alpha = 0.95, beta = 2, min_samples_leaf = 5)
variance_forest_params <- list(num_trees = 50, alpha = 0.95,
beta = 1.25, min_samples_leaf = 5)
bart_model_mcmc <- stochtree::bart(
X_train = X_train, y_train = y_train, X_test = X_test,
num_gfr = num_gfr, num_burnin = num_burnin, num_mcmc = num_mcmc,
general_params = general_params, mean_forest_params = mean_forest_params,
variance_forest_params = variance_forest_params
)Inspect the MCMC samples
plot(rowMeans(bart_model_mcmc$y_hat_test), y_test,
pch=16, cex=0.75, xlab = "pred", ylab = "actual", main = "mean function")
abline(0,1,col="red",lty=2,lwd=2.5)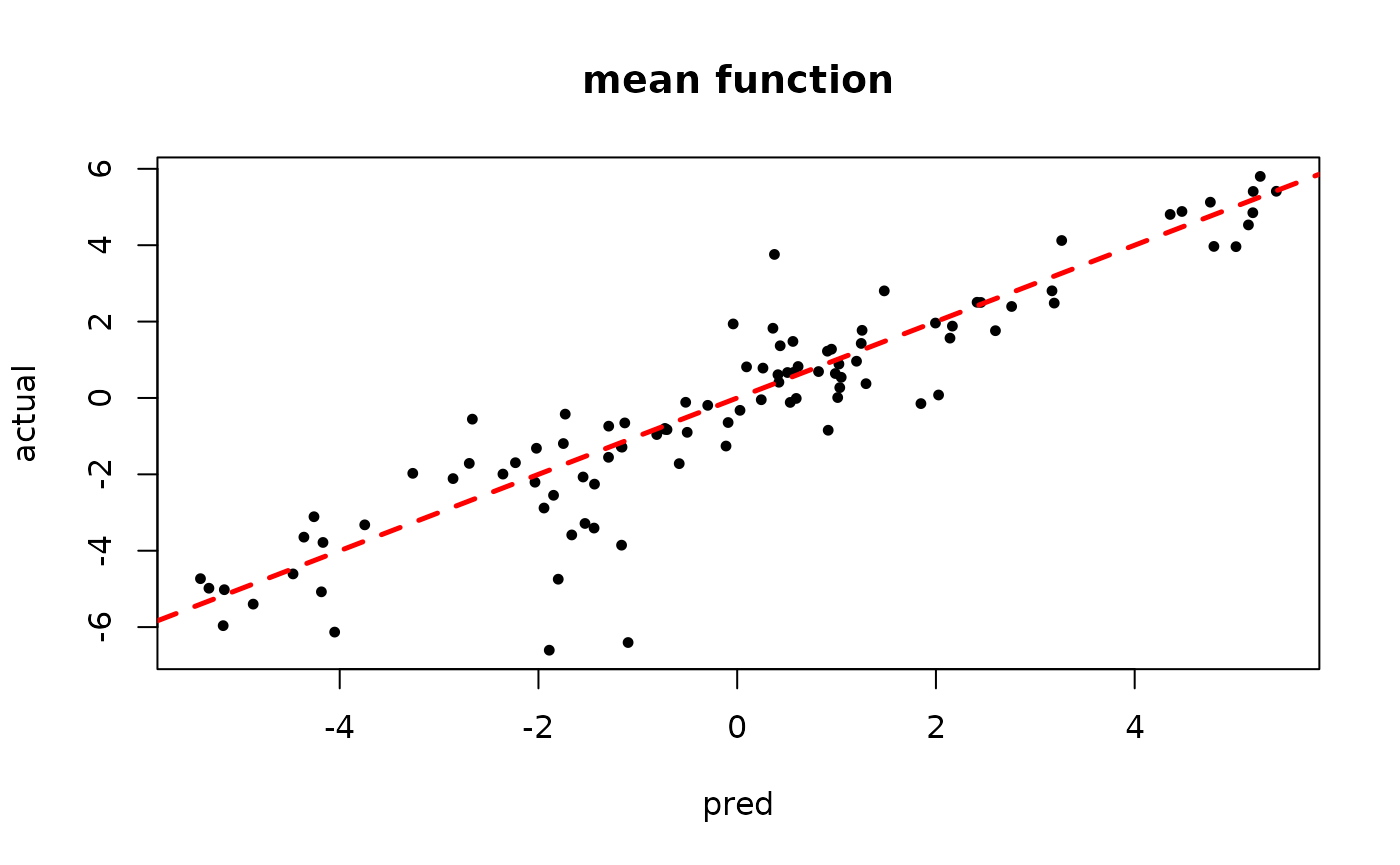
plot(rowMeans(bart_model_mcmc$sigma2_x_hat_test), s_x_test^2,
pch=16, cex=0.75, xlab = "pred", ylab = "actual", main = "variance function")
abline(0,1,col="red",lty=2,lwd=2.5)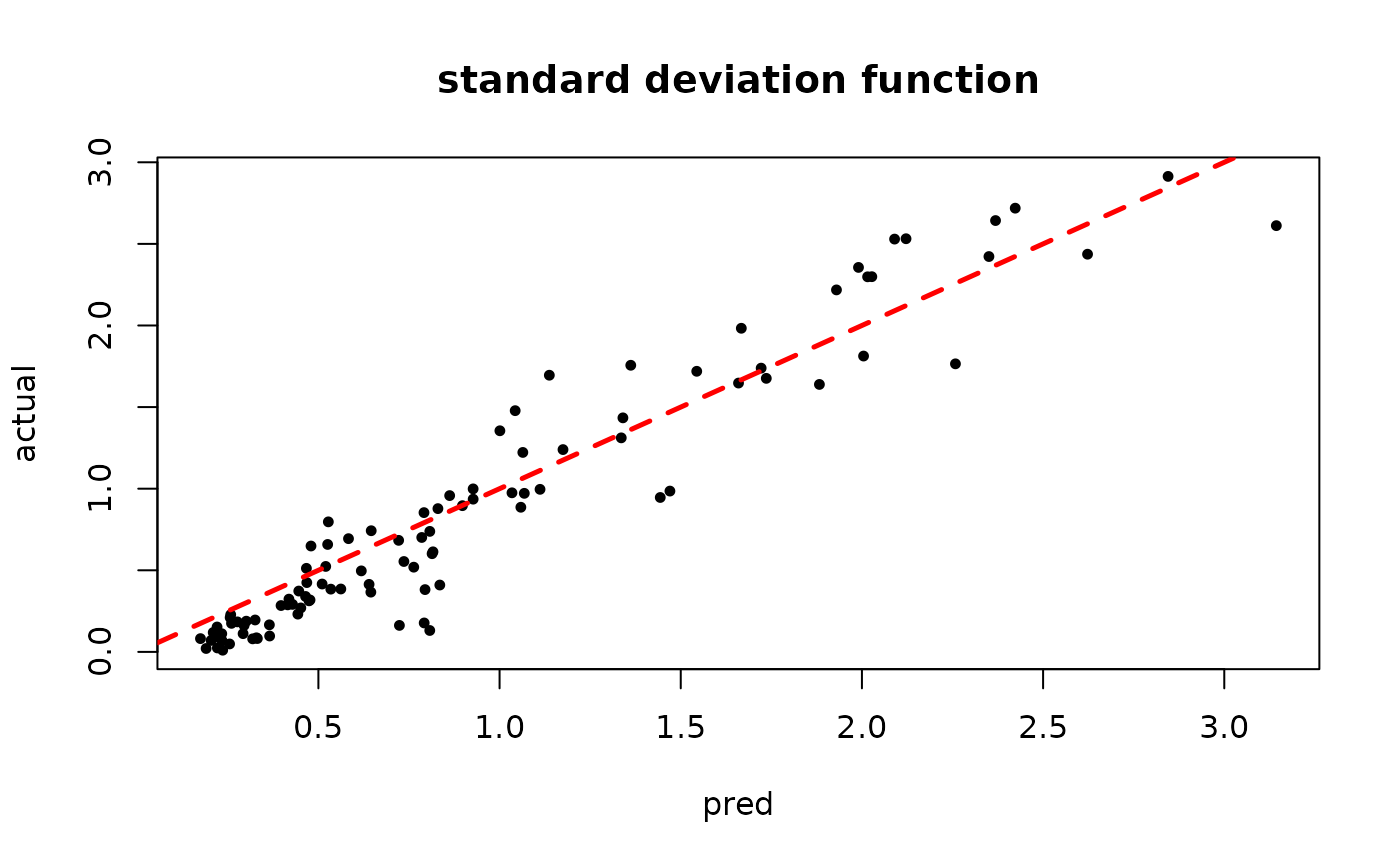
Section 2: Causal Inference
Demo 1: Heterogeneous Treatment Effect, Continuous Treatment, Heteroskedastic Errors
We consider the following data generating process:
Simulation
We draw from the DGP defined above
n <- 2000
x1 <- rnorm(n)
x2 <- rnorm(n)
x3 <- rnorm(n)
x4 <- rnorm(n)
x5 <- rnorm(n)
X <- cbind(x1,x2,x3,x4,x5)
p <- ncol(X)
mu_x <- 1 + 2*x1 - 4*(x2 < 0) + 4*(x2 >= 0) + 3*(abs(x3) - sqrt(2/pi))
tau_x <- 1 + 2*x4
u <- runif(n)
pi_x <- ((mu_x-1)/4) + 4*(u-0.5)
Z <- pi_x + rnorm(n,0,1)
E_XZ <- mu_x + Z*tau_x
s_X <- (
((0 <= X[,1]) & (0.25 > X[,1])) * (0.5) +
((0.25 <= X[,1]) & (0.5 > X[,1])) * (1) +
((0.5 <= X[,1]) & (0.75 > X[,1])) * (2) +
((0.75 <= X[,1]) & (1 > X[,1])) * (3)
)
y <- E_XZ + rnorm(n, 0, 1)*s_X
X <- as.data.frame(X)
# Split data into test and train sets
test_set_pct <- 0.2
n_test <- round(test_set_pct*n)
n_train <- n - n_test
test_inds <- sort(sample(1:n, n_test, replace = FALSE))
train_inds <- (1:n)[!((1:n) %in% test_inds)]
X_test <- X[test_inds,]
X_train <- X[train_inds,]
pi_test <- pi_x[test_inds]
pi_train <- pi_x[train_inds]
Z_test <- Z[test_inds]
Z_train <- Z[train_inds]
y_test <- y[test_inds]
y_train <- y[train_inds]
mu_test <- mu_x[test_inds]
mu_train <- mu_x[train_inds]
tau_test <- tau_x[test_inds]
tau_train <- tau_x[train_inds]
s_x_test <- s_X[test_inds]
s_x_train <- s_X[train_inds]Sampling and Analysis
Warmstart
We first simulate from an ensemble model of
using “warm-start” initialization samples (Krantsevich, He, and Hahn (2023)). This is the
default in stochtree.
num_gfr <- 10
num_burnin <- 0
num_mcmc <- 100
num_samples <- num_gfr + num_burnin + num_mcmc
general_params <- list(keep_every = 5)
prognostic_forest_params <- list(sample_sigma2_leaf = F)
treatment_effect_forest_params <- list(sample_sigma2_leaf = F)
variance_forest_params <- list(num_trees = num_trees)
bcf_model_warmstart <- bcf(
X_train = X_train, Z_train = Z_train, y_train = y_train, propensity_train = pi_train,
X_test = X_test, Z_test = Z_test, propensity_test = pi_test,
num_gfr = num_gfr, num_burnin = num_burnin, num_mcmc = num_mcmc,
general_params = general_params, prognostic_forest_params = prognostic_forest_params,
treatment_effect_forest_params = treatment_effect_forest_params,
variance_forest_params = variance_forest_params
)
#> Warning in bcf(X_train = X_train, Z_train = Z_train, y_train = y_train, :
#> Adaptive coding is only compatible with binary (univariate) treatment and, as a
#> result, will be ignored in sampling this model
#> Warning in bcf(X_train = X_train, Z_train = Z_train, y_train = y_train, :
#> Global error variance will not be sampled with a heteroskedasticityInspect the BART samples that were initialized with an XBART warm-start
plot(rowMeans(bcf_model_warmstart$mu_hat_test), mu_test,
xlab = "predicted", ylab = "actual", main = "Prognostic function")
abline(0,1,col="red",lty=3,lwd=3)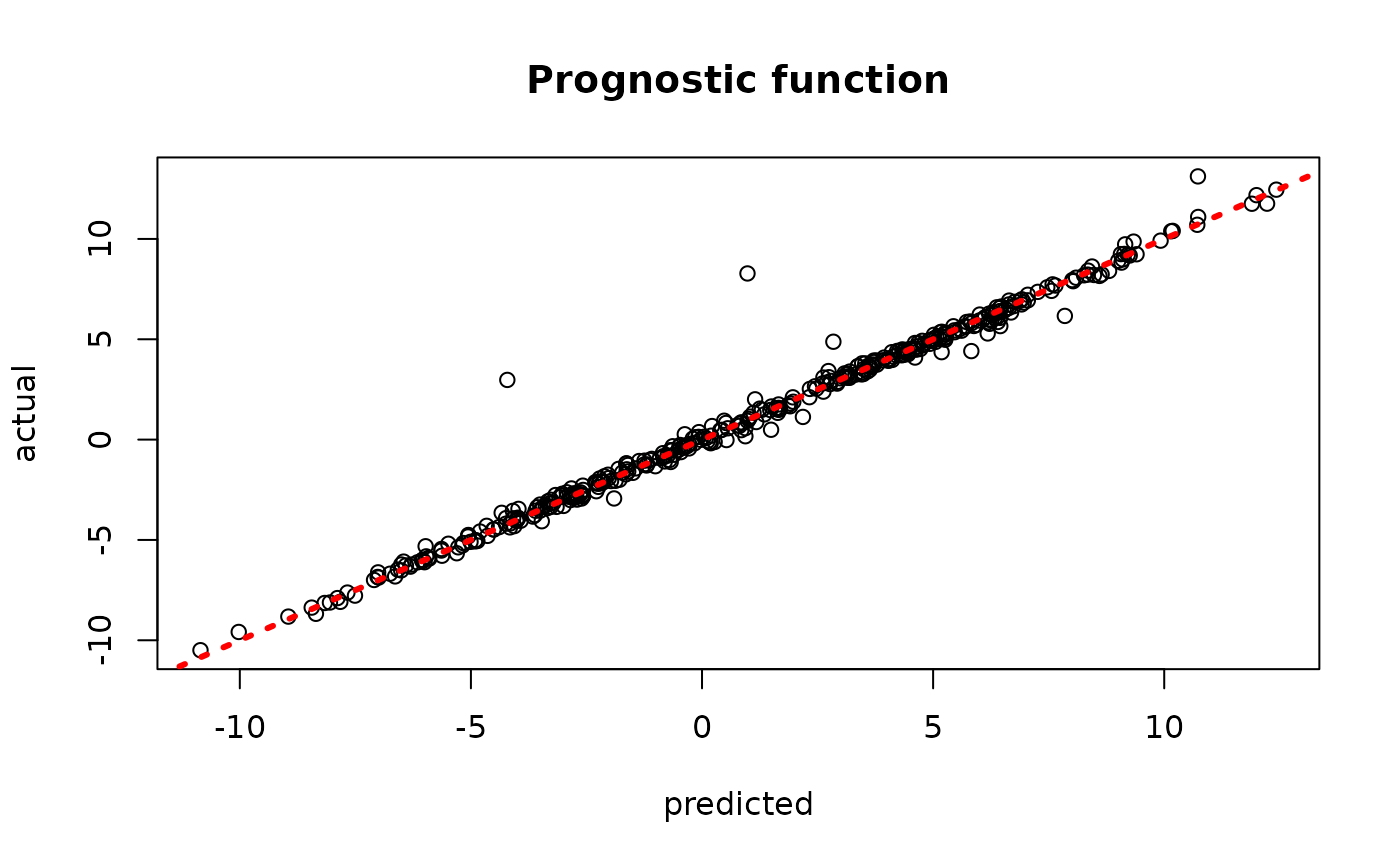
plot(rowMeans(bcf_model_warmstart$tau_hat_test), tau_test,
xlab = "predicted", ylab = "actual", main = "Treatment effect")
abline(0,1,col="red",lty=3,lwd=3)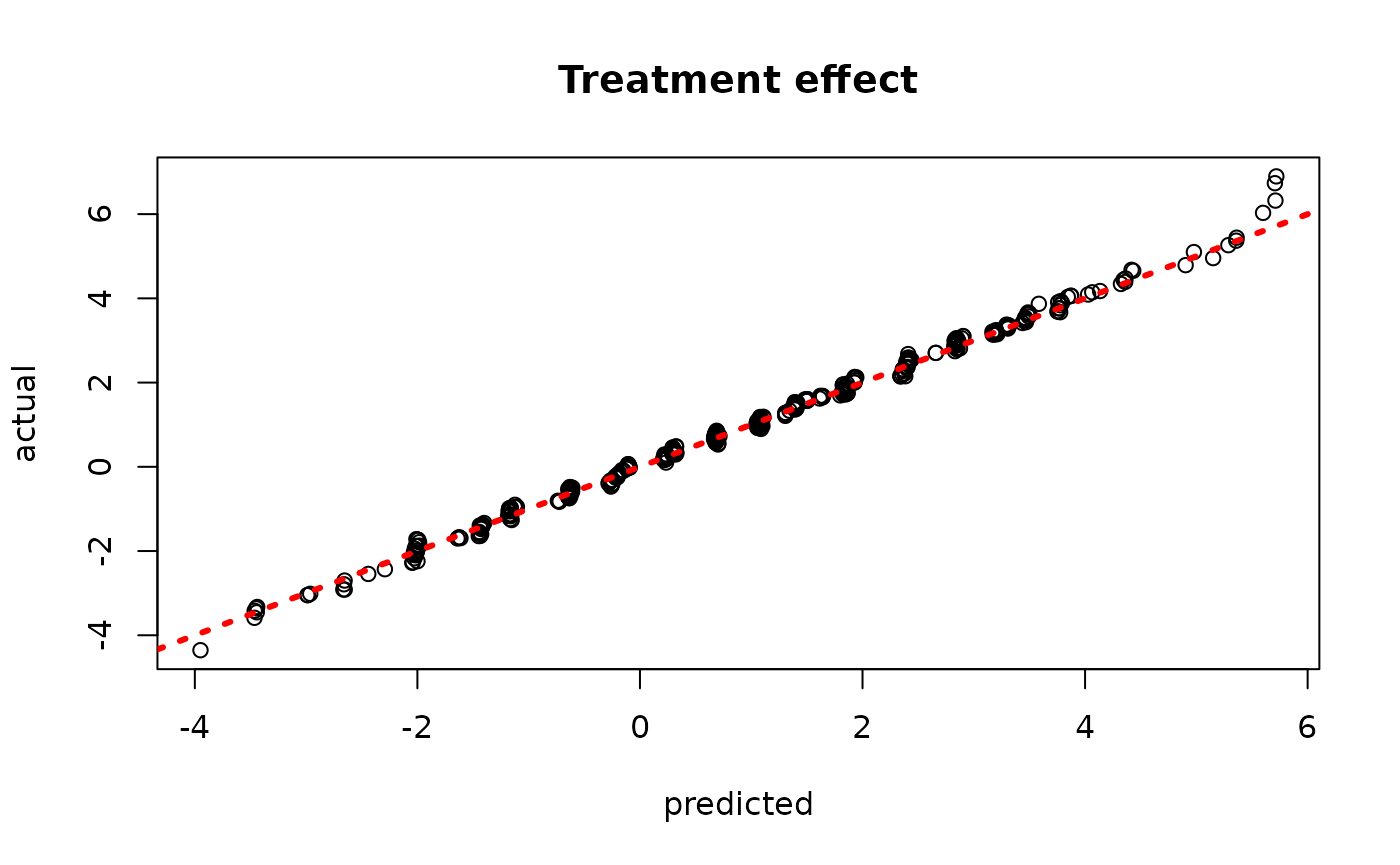
plot(rowMeans(bcf_model_warmstart$sigma2_x_hat_test), s_x_test^2,
pch=16, cex=0.75, xlab = "pred", ylab = "actual", main = "variance function")
abline(0,1,col="red",lty=2,lwd=2.5)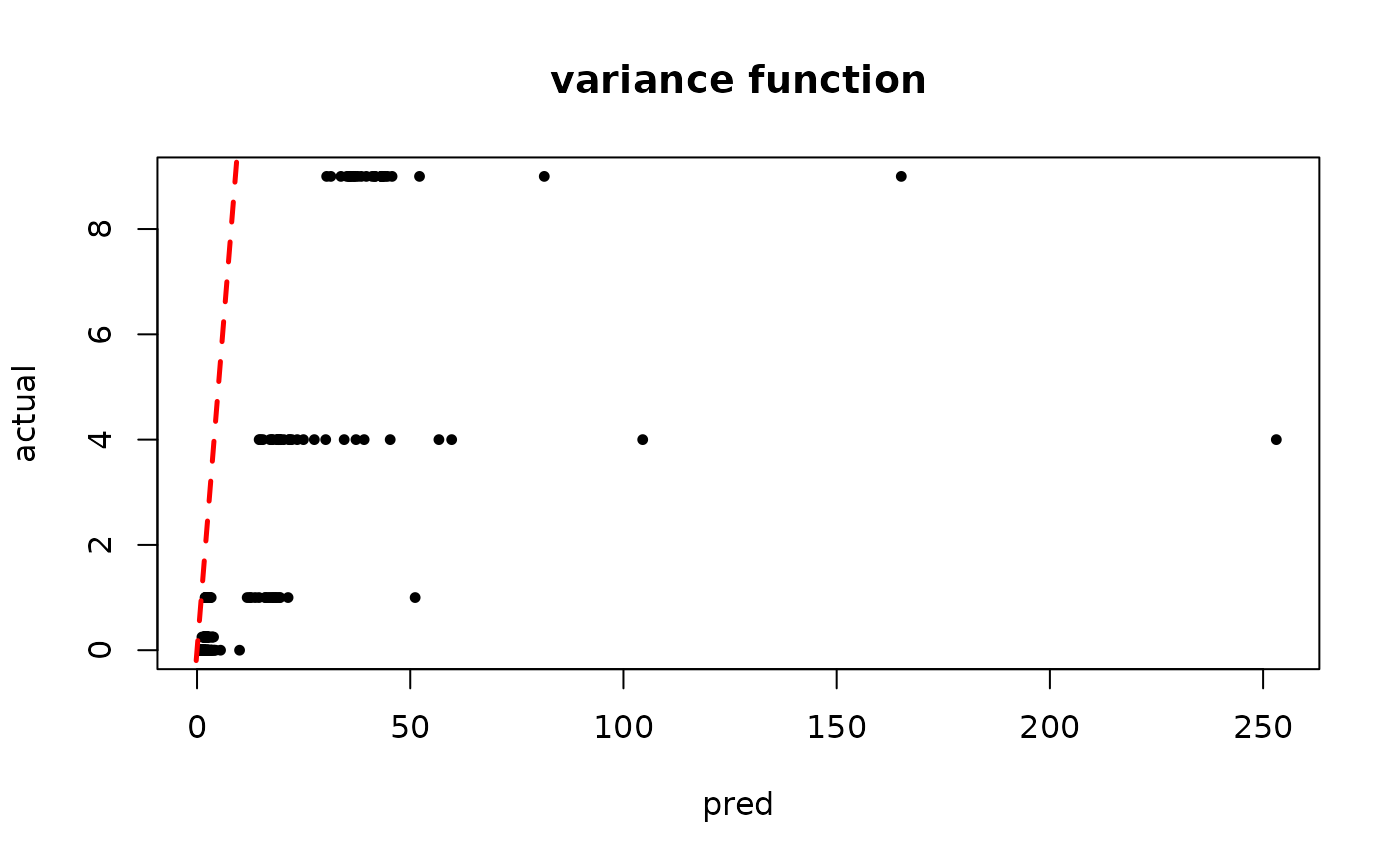
BART MCMC without Warmstart
Next, we simulate from this ensemble model without any warm-start initialization.
num_gfr <- 0
num_burnin <- 2000
num_mcmc <- 100
num_samples <- num_gfr + num_burnin + num_mcmc
general_params <- list(keep_every = 5)
prognostic_forest_params <- list(sample_sigma2_leaf = F)
treatment_effect_forest_params <- list(sample_sigma2_leaf = F)
variance_forest_params <- list(num_trees = num_trees)
bcf_model_root <- bcf(
X_train = X_train, Z_train = Z_train, y_train = y_train, propensity_train = pi_train,
X_test = X_test, Z_test = Z_test, propensity_test = pi_test,
num_gfr = num_gfr, num_burnin = num_burnin, num_mcmc = num_mcmc,
general_params = general_params, prognostic_forest_params = prognostic_forest_params,
treatment_effect_forest_params = treatment_effect_forest_params,
variance_forest_params = variance_forest_params
)
#> Warning in bcf(X_train = X_train, Z_train = Z_train, y_train = y_train, :
#> Adaptive coding is only compatible with binary (univariate) treatment and, as a
#> result, will be ignored in sampling this model
#> Warning in bcf(X_train = X_train, Z_train = Z_train, y_train = y_train, :
#> Global error variance will not be sampled with a heteroskedasticityInspect the BART samples after burnin
plot(rowMeans(bcf_model_root$mu_hat_test), mu_test,
xlab = "predicted", ylab = "actual", main = "Prognostic function")
abline(0,1,col="red",lty=3,lwd=3)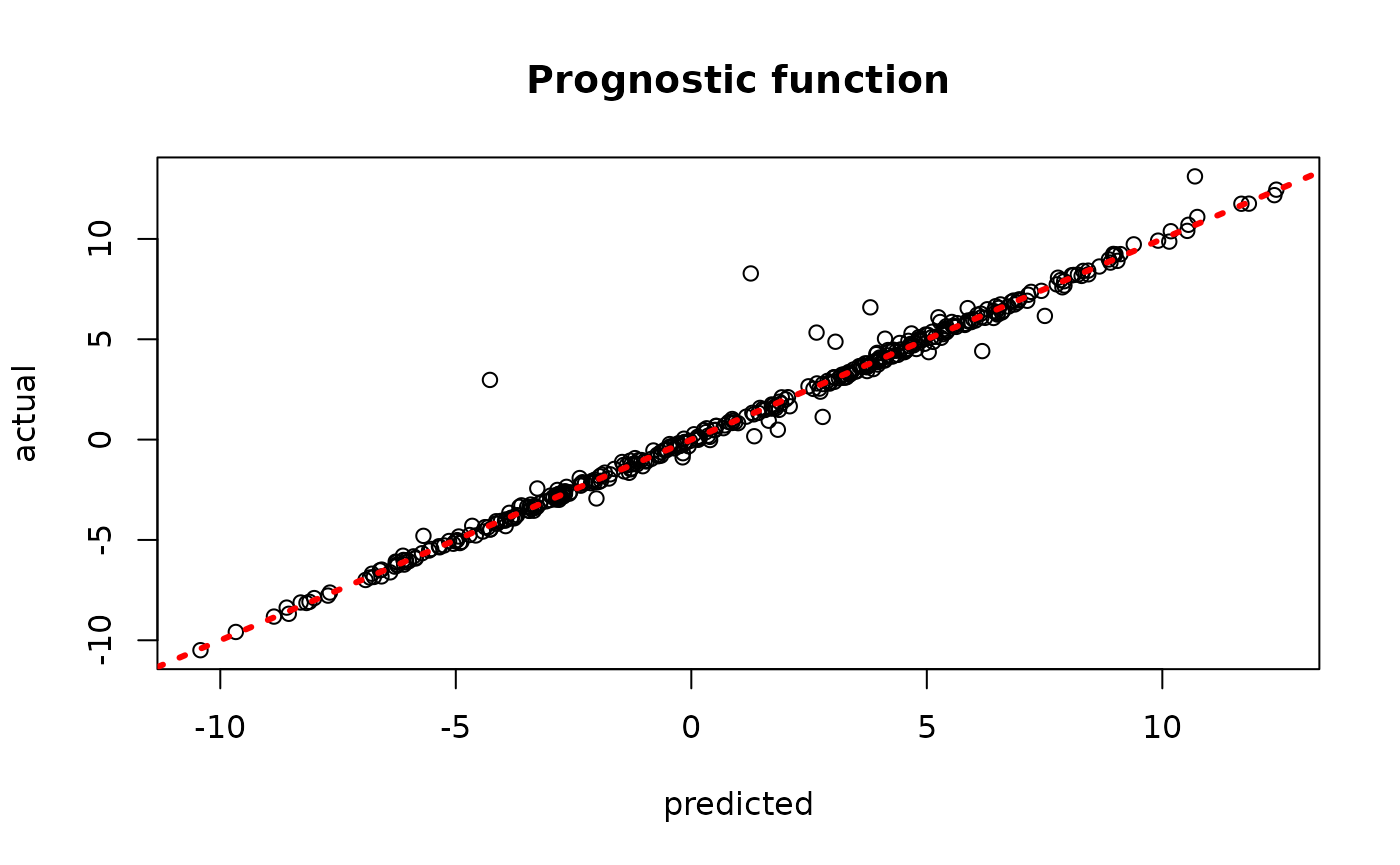
plot(rowMeans(bcf_model_root$tau_hat_test), tau_test,
xlab = "predicted", ylab = "actual", main = "Treatment effect")
abline(0,1,col="red",lty=3,lwd=3)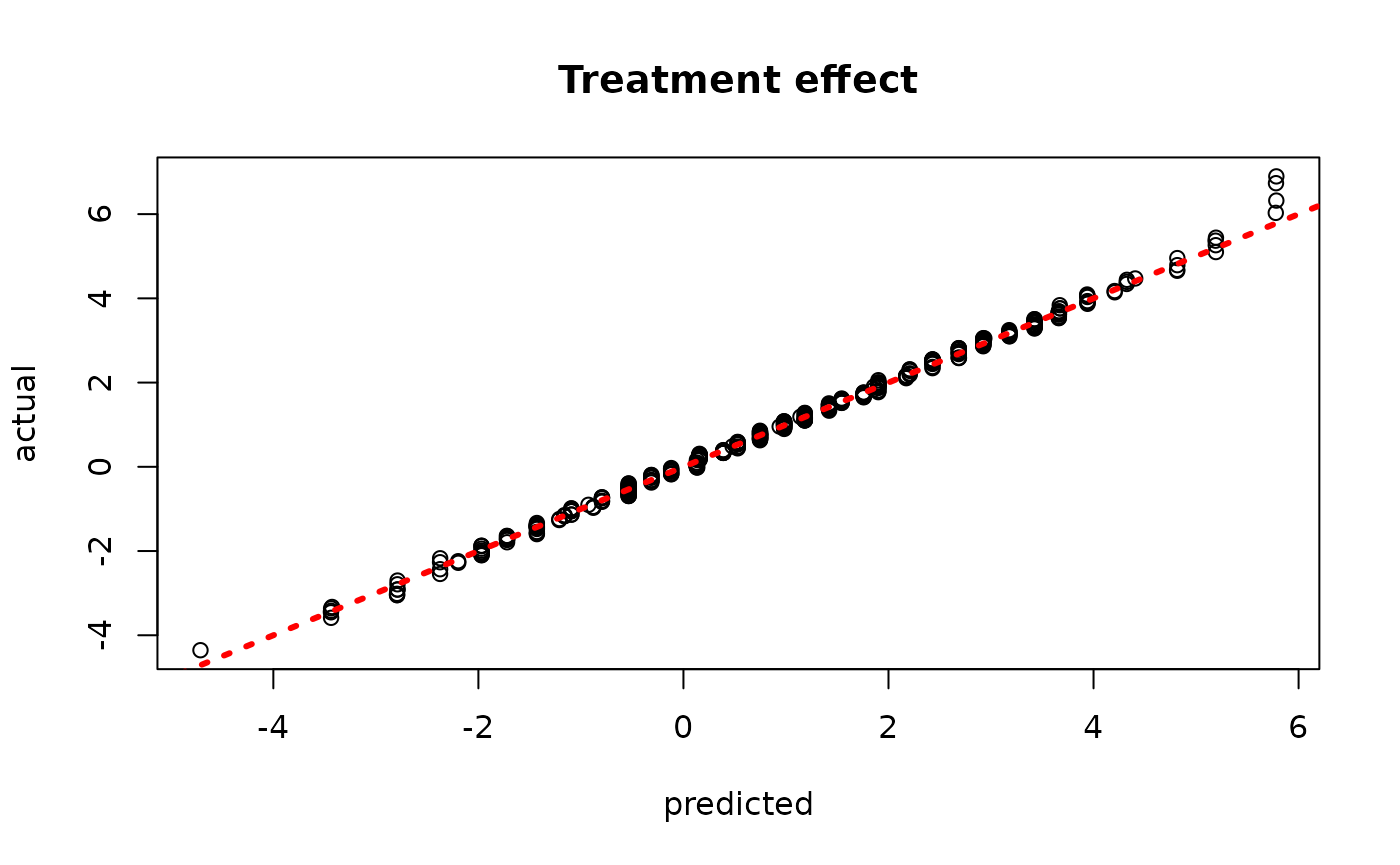
plot(rowMeans(bcf_model_root$sigma2_x_hat_test), s_x_test^2,
pch=16, cex=0.75, xlab = "pred", ylab = "actual", main = "variance function")
abline(0,1,col="red",lty=2,lwd=2.5)